New Doctoral Research Published: Mesh Morphing-Driven Strategies for Real-Time Multi-Physics Design Optimization
 Written by rbfLAB on
Written by rbfLAB on
We are pleased to announce the publication of the doctoral dissertation by Andrea Lopez, titled “Integrated Multi-Physics and Multi-Fidelity Methodologies for Digital Twin Applications”. This research was developed within the PhD program in Design, Manufacturing, and Operations Engineering (Cycle XXXVII) at the University of Rome Tor Vergata.
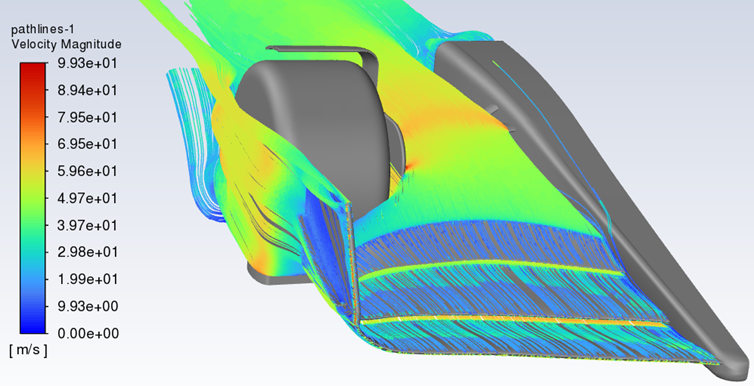
This work presents a significant advancement in the application of Radial Basis Function (RBF) Morphing technology to next-generation engineering design workflows. Focusing on the integration of simulation, optimization, and real-time feedback, the dissertation outlines new approaches for embedding RBF into interactive digital twin frameworks.
Core Contributions
- High-Fidelity Mesh Morphing: Implementation of precise shape modification strategies to support robust optimization processes.
- Multi-Physics Coupling: Seamless integration of fluid-structure interaction models using morphing-based interpolation schemes.
- Multi-Fidelity Bridging: Efficient data mapping and consistency enforcement between low- and high-fidelity simulations.
- Real-Time Sensitivity Analysis: Deployment of adjoint methods and reduced-order models (ROMs) for fast, responsive design iterations.
Through these contributions, the research demonstrates how Radial Basis Functions Mesh Morphing enables enhanced control and flexibility in computational modeling, making it a powerful asset for digital twin technologies across aerospace and industrial domains.
🔗 Access the full dissertation here: https://www.rbf-morph.com/multi-physics-and-multi-fidelity-approaches-for-digital-twin-integration-2/




Comments